The Role of Financial Regulation in Forex Trading
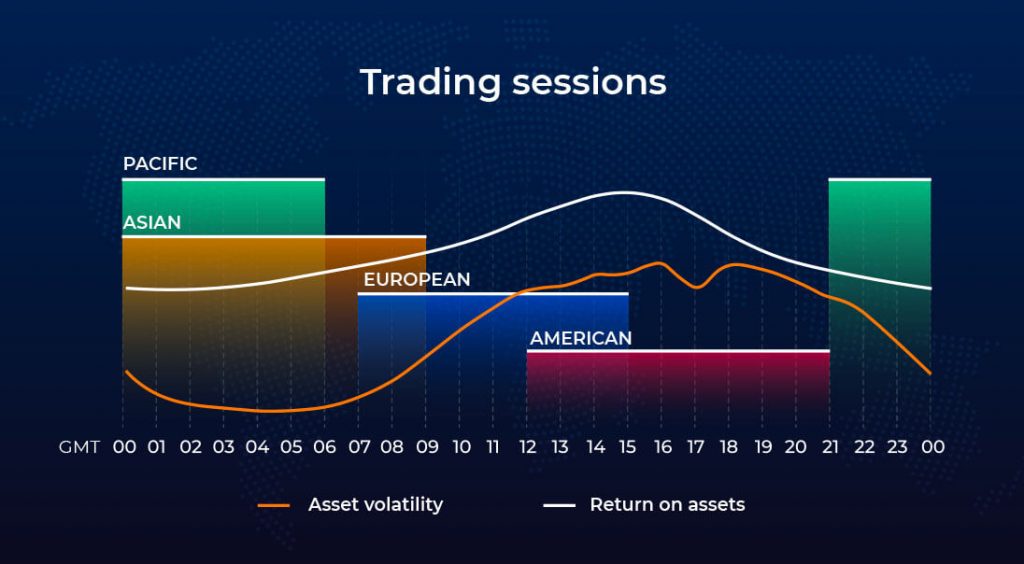
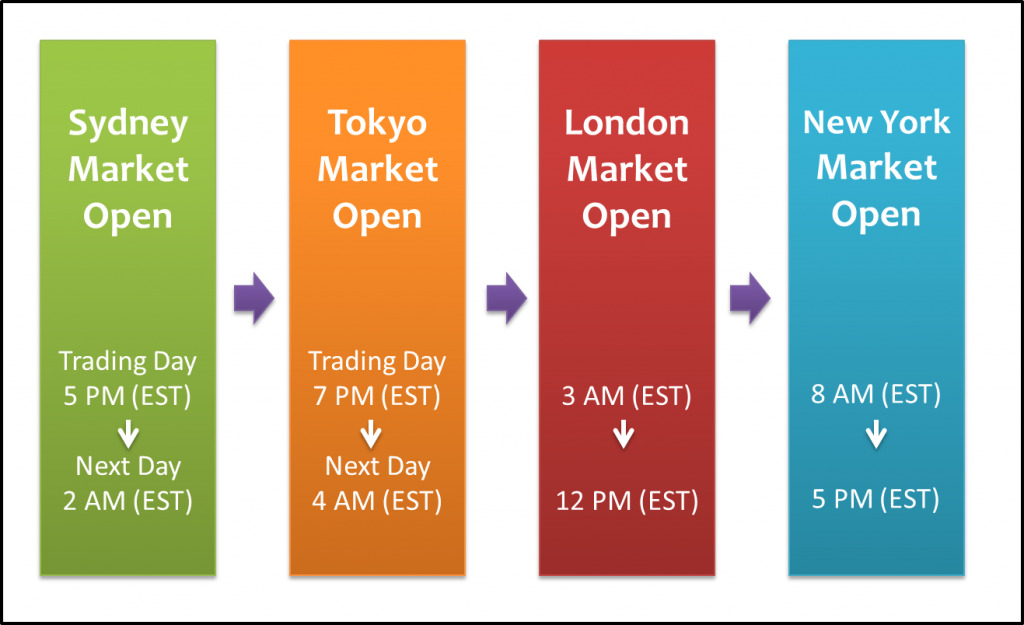
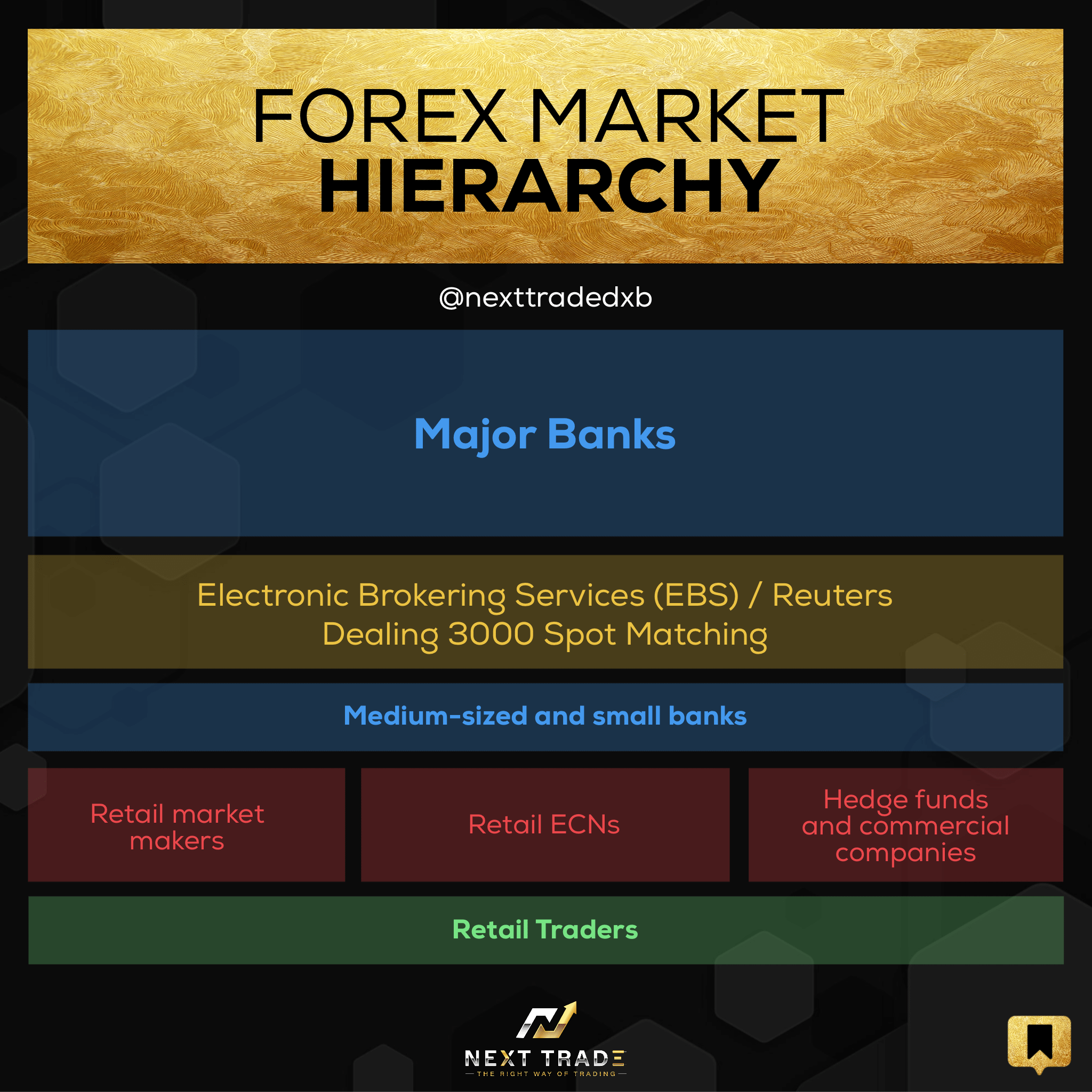
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, involves the buying and selling of currencies. It is a decentralized global market where participants trade various currencies based on their value relative to one another. As with any financial market, there is a need for regulation to ensure fair practices and protect investors.
The role of financial regulation in forex trading is crucial for maintaining stability, transparency, and investor confidence in the market. Regulatory bodies around the world play a significant role in overseeing and supervising forex brokers, traders, and other market participants.
1. Protecting Investors
Financial regulations aim to protect investors from fraudulent activities, scams, and unfair practices in the forex market. Regulations often require forex brokers to operate with transparency, providing detailed information about their services, fees, and risks involved. This helps investors make informed decisions and reduces the likelihood of falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
2. Ensuring Market Stability
Financial regulations help maintain market stability by setting standards and guidelines for forex trading. These regulations ensure that market participants adhere to certain rules and practices that promote fairness, prevent market manipulation, and discourage excessive speculation. By promoting stability, regulators help reduce the risk of systemic failures that can have far-reaching consequences.
3. Mitigating Risks
Forex trading involves inherent risks, such as price fluctuations, liquidity risks, and counterparty risks. Regulatory bodies impose regulations on forex brokers to mitigate these risks and protect traders. For example, regulations may require brokers to maintain a minimum capital requirement to ensure they have sufficient funds to handle client transactions and potential losses.
4. Monitoring Compliance
Regulatory bodies monitor compliance with forex regulations through periodic reviews, audits, and inspections of market participants. They ensure that brokers are following the outlined rules and guidelines, preventing fraudulent activities, and protecting investors’ interests. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, or even revocation of licenses.
5. Enhancing Market Transparency
Financial regulations promote transparency in the forex market by requiring brokers to provide accurate and timely information to traders. This includes disclosing transaction costs, spreads, leverage ratios, and any potential conflicts of interest. Transparent practices help traders assess the risks involved and make informed decisions.
6. Resolving Disputes
In cases of disputes between traders and brokers, regulatory bodies often act as mediators or arbitrators. They provide a platform for fair resolution of conflicts, ensuring that both parties have an opportunity to present their case. This helps maintain trust and confidence in the market, knowing that there is a mechanism to address grievances.
In conclusion, financial regulation plays a vital role in the forex market. It protects investors, ensures market stability, mitigates risks, monitors compliance, enhances transparency, and resolves disputes. By implementing and enforcing regulations, regulatory bodies contribute to a safer and more reliable environment for forex trading.